10 Study Skills IEP Goals (including Note Taking)
I’m a good learner, but I’m terrible at studying. Always have been. Other than re-reading chapters and notes and rote memorization, I never knew what studying was.
No one ever taught me study skills. It was just expected that all students knew how to study and learn. I still often find that it doesn’t occur to many IEP teams to create study skills IEP goals, only study skills accommodations.

I think many students struggle with study skills, particularly if you have an IEP and/or struggle with executive functioning skills. If a student lacks a skill, you either have to teach the skill or make accommodations for lack of skill.
Organization/Study Skills IEP Goals
That’s a decision that should be made within the IEP team. It’s important to involve the student to the maximum extent possible. For example, if a child struggles with working memory, there are exercises and tasks that they can do to improve it.
However, at some point the team needs to decide if it is more important for a student to be able to recall the information from memory, or know where to find that information in their notes or textbook.
What’s more important–the ability to have 100% retrieval from memory, or knowing where to find the information and how to apply it?
One of the more common requests I get is for IEP goals for Study Skills. So, I’ve compiled a list of Study Skills IEP Goals, as well as some accommodation ideas and resources where you can go to find more assistance.

Examples of Study Skills
Study skills refer to a set of strategies and techniques that students use to enhance their learning and academic performance. Developing effective study skills is crucial for success in education, as they can help students manage their time efficiently, retain information, and perform well on exams. Here are some key study skills:
- Time Management:
- Create a schedule or timetable to allocate dedicated time for studying, attending classes, and other activities.
- Break larger tasks into smaller, more manageable chunks to avoid feeling overwhelmed.
- Prioritize tasks based on deadlines and importance.
- Note-Taking:
- Develop effective note-taking techniques, such as summarizing information, using bullet points, and highlighting key concepts.
- Organize notes in a clear and coherent manner to facilitate later review.
- Active Reading:
- Engage with the material actively by asking questions, making predictions, and connecting new information to prior knowledge.
- Take breaks during reading sessions to enhance focus and understanding.
- Effective Reading Strategies:
- Skim and scan texts to get an overview before in-depth reading.
- Highlight or underline key points and important details.
- Take notes while reading to reinforce understanding.
- Memory Techniques:
- Use mnemonic devices, acronyms, or visualization to aid memory retention.
- Practice retrieval by testing yourself on the material regularly.
- Critical Thinking:
- Analyze and evaluate information rather than simply memorizing it.
- Develop the ability to think critically and make connections between concepts.
- Problem-Solving:
- Practice solving problems related to the subject matter.
- Seek help when encountering challenging concepts or questions.
- Active Participation:
- Actively participate in class discussions, ask questions, and seek clarification when needed.
- Collaborate with peers through study groups or discussion forums.
- Effective Communication:
- Develop communication skills for writing essays, reports, and other assignments.
- Clearly articulate ideas and arguments.
- Self-Reflection:
- Reflect on your learning process and identify areas for improvement.
- Adjust study strategies based on what works best for you.
- Test-Taking Strategies:
- Practice past exams or sample questions under timed conditions.
- Review and understand feedback on previous assessments.
To be successful, students often have to use multiple EF skills in the same situation, which is often difficult.
Study Skills IEP Goals
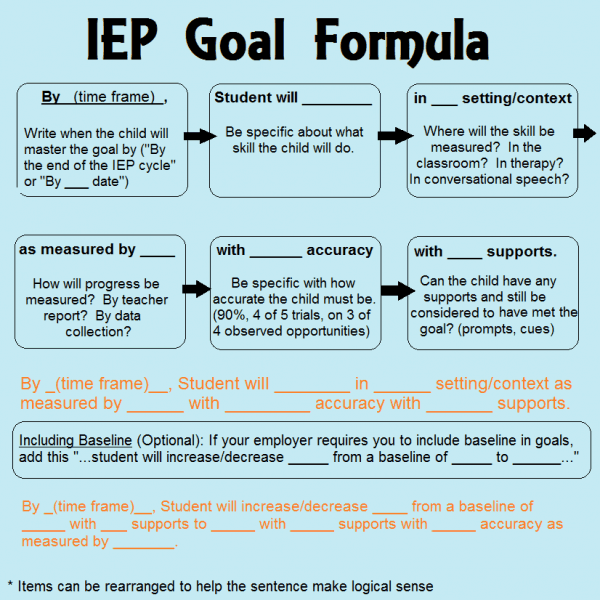
Remember that you have to add in absolutes to make these measurable. I’ve included the IEP Goal Formula at the bottom of this post, but these 10 items will get you started.
Also, I have an IEP Goal Bank if you need more ideas.
- Given the content areas of study, Student will be able to anticipate and verbalize/list X number of test questions.
- Student will be able to identify X number of concerns that lead to test anxiety and brainstorm 1-2 solutions for each.
- Given a calendar and content materials, student will be able to plot out study sessions to follow.
- Student will self-identify X number of concepts that he/she is struggling to master and ask for assistance.
- At the end of a study session, student will be able to verbalize X number of concepts or facts that were reviewed.
- Student will be able to identify X number of items that are a distraction while studying and develop a remedy for each.
- Given a list of options, student will identify which methods work best for learning material and concepts. (IE- graphic organizers, having someone read material, watching video, discussion)
- When given an already graded/corrected test, student will review with tutor/teacher the incorrect answers and where correct information can be found. (can also include identifying strategies for next time)
- Student will self-identify their most successful method of reading and note-taking and develop a strategy for each.
- Student will be able to self-identify their best environment for test-taking. (quiet room, being able to talk out loud, verbal test, sensory break beforehand, etc.)
Examples of Study Skills Goals by Age
Elementary School Goals
- Organization: By the end of the school year, Sally will use color-coded folders to sort and file completed assignments in 4 out of 5 opportunities with minimal adult prompts.
- Time Management: Using a visual timer, Sam will complete 3 out of 4 assigned class tasks within the allotted time frame across three consecutive weeks.
Middle School Study Skills Goals
- Note-Taking: During science class, Alex will use a provided graphic organizer to take notes on key concepts, achieving at least 80% accuracy as measured by teacher review.
- Homework Completion: By the end of the semester, Mia will submit all homework assignments on time for four consecutive weeks using a homework checklist system.
High School Study Skills Goals
- Prioritization: By the end of the school year, Jake will use a prioritization tool (like a to-do list or planner) to rank assignments in order of importance and complete high-priority tasks in 3 out of 4 instances during study hall periods.
- Self-Advocacy: In preparation for tests, Kelly will independently request additional study materials or support in 3 out of 4 opportunities when she identifies a need for clarification.
What Makes a Good Study Skills IEP Goal?
A good goal starts with data. Schools often try to write vague goals like “improve organization” or “stay on task.” Not good enough. You’ll want goals that:
- Are specific.
- Can be tracked with clear data.
- Include benchmarks to measure progress.
Here’s an example of a meh goal:
“Johnny will improve his study skills 80% of the time.”
What does that even mean? Who’s measuring it? How do we know if Johnny’s skills improved by 80%? We don’t.
Now, here’s an awesome goal:
“By June 2024, Johnny will independently use a daily planner to record homework assignments and identify due dates in 4 out of 5 instances as observed and documented by his special education teacher.”
See the difference? It’s clear, measurable, and has built-in accountability.
Note Taking IEP Goals
Many students are expected to take notes during a class or lecture but have no idea what to write down. To be an effective note-taker, you must have competent receptive language. This includes voice, body language, expressions, volume, etc.
Once the student can do that, they must be able to extract what is (seemingly) important and write it down. And write it down so that it can be referred to later and understood in context.
This is a pretty high-level executive functioning skill. And why it is such a struggle for so many kids with learning disabilities.
I would be irresponsible to list IEP goals for note-taking, when those goals are the ultimate.
So much foundational content must be mastered first. I recommend you do a deep dive with the students to pinpoint their issues and accommodate their lack of skill until they learn how to take notes.
- Emotional Self-Regulation IEP Goals
- Study Skills IEP Goals
- Focus and Attention IEP Goals
- Inference IEP Goals
- Working Memory IEP Goals
- Task Initiation IEP Goals
- Impulse Control IEP Goals
- Work Completion IEP Goals
- Executive Functioning IEP Goals
- Free IEP Goal Bank with 1000+ Measurable IEP Goals and Objectives separated by Domain



