50 Self Advocacy IEP Goals for Every Grade: Measurable Examples to Use Now
Every student should learn how to speak up for themselves—especially IEP students. If more of our kids knew how to ask for a sensory break or say, “I need help,” so many behavior issues could be avoided. The truth is, we won’t always be there to advocate for them. But we can teach them how to do it for themselves—and that starts with self-advocacy IEP goals.

In the context of IEPs, self-advocacy involves:
- Participating in decisions that affect one’s education
- Understanding one’s disability, including strengths and weaknesses
- Knowing what accommodations and modifications are available and how to request them
- Effectively communicating needs to teachers and peers
What this will look like in day to day practice will vary by the student’s abilities. Even students with a lot of needs can be taught to self advocate. For example, my son cannot speak. However, when he feels a seizure coming on, he often will sit on the ground (no matter where he is!) and refuse to budge. What initially was seen as non-compliance or task refusal is actually an important message he is communicating.
What is Self Advocacy?
Self-advocacy is the ability to understand your own needs and effectively communicate those needs to others. For students with disabilities, this skill becomes particularly important in academic, social, and eventually employment settings. Self Advocacy goes hand in hand with Self Determination, which is: “the process by which a person controls their own life.”
I can only imagine how exhausting, disheartening, and deflating it must be to be for some of our kids. People are always talking about you, your faults, your disabilities, your shortcomings, and your negative behaviors. Telling you what you need to do. And how often do we let them participate in the process? A child should participate in their IEP process from the earliest age possible that it is appropriate. While IDEA requires that students who are IEP transition age be invited to the IEP meeting, I see very few of them attend or give meaningful input. Certainly, that responsibility is on the parents.
Self-determination is often talked about at transition time, but not much outside of that. What a huge mistake! When our kids leave the school system or leave the home, they don’t miraculously develop the ability to self-advocate. This is something that should be worked on and weaved into everything.
It’s also essential that you and your child have a vision, and that the student has participated in developing the vision. I always say, “The IEP is the roadmap, the IEP Vision Statement is the destination. So how can you develop a roadmap if you don’t know where you’re going?” I have a free IEP Vision Statement workbook in that link. It’s designed to be a family activity, but certainly could be done with a student and their case manager or counselor.
Self Advocacy IEP Goal Example
Both parents and educators can be intimidated by adding goals like these because they seem to be challenging to measure. Or at least that is the perception. It can be quite simple to measure; just add a quantity. I have a formula chart at the end of the post.
If a child has a behavior plan as part of their IEP, then it is absolutely necessary that they have self-advocacy goals. A student cannot stay on a behavior plan forever or have adults intervening and removing your antecedents when they can. A student needs to be able to self-identify their antecedents, predict them and have an action plan of acceptable coping skills. Set specific, attainable self-advocacy goals in the IEP.
What is an example of an IEP goal for self-advocacy?
I have over 50 examples of an IEP goal for self-advocacy below, separated by category or domain.
Self Advocacy IEP Goals: Self Awareness
- Goal: Student can communicate an understanding of the goals on the IEP. (read over with them and discuss) Objective: The student will accurately explain two academic or behavioral goals listed on their IEP, including the purpose and methods for achieving each goal, during a discussion with the teacher or support staff, with 80% accuracy.
- Demonstrate an understanding of what a learning disability (or other condition if appropriate) is and able to communicate to others how he/she learns best.
- Demonstrate an understanding of what their learning disability is and communicate to others what he/she needs to learn successfully.
- Describe student strengths accurately.
- List possible antecedents to their own behaviors (“I get upset when…..”) and list possible acceptable alternatives to their negative behavior.
Self Advocacy IEP Goals: Personal Choices
Depending on the student and their challenges, you may have to change up these goals. Some students are impulsive and don’t think about choices before they make them–resulting in preventable mistakes, or not learning from their mistakes. Others may overthink a choice, and never come to a conclusion.
- Given the school lunch menu, I will select between the two options available that day in 4 out of 5 trials.
- If I have five elective class options, I will select one class per semester for my schedule.
- Make decisions between two or more choices.
- The student will identify two available options in a given classroom scenario (e.g., choosing between tasks or tools) and make a choice that aligns with their preferences in 4 out of 5 opportunities, as measured by teacher observation.
- When presented with multiple options for completing an assignment or activity, the student will verbally or nonverbally communicate their choice and explain their reasoning in 3 out of 4 weekly opportunities.
- The student will demonstrate the ability to make a personal choice (e.g., selecting a preferred break activity, choosing seating, or requesting a support) and follow through independently in 80% of opportunities.
- During structured decision-making activities, the student will identify one potential consequence for each option and select the one that best meets their learning needs, with no more than one prompt, in 4 out of 5 sessions.
- The student will complete a weekly reflection activity where they describe one choice they made during the week, why they made it, and whether they feel it was successful, with 80% accuracy.
Self Advocacy IEP Goals: IEP Meeting Participation
I am a huge advocate of students attending their IEP meetings, and participating in their IEP meetings. A student should participate in their IEP meeting, at the youngest age possible, to the maximum extent possible. What that will look like for each child is different.
- Goal: Co-lead annual review and help develop IEP goals. Objective: The student will actively participate in annual IEP meetings by contributing ideas and preferences for their educational goals, as observed by meeting participants and documented in meeting notes.
- Lead annual IEP meetings to help develop goals. (YES! I do know of some kids who do this! It can be done!)
- Participate in school meetings (parent/teacher conference or annual review) and advocate for self with the support of parent and teachers.
- The student will attend their IEP meeting and share one personal strength and one area of need with no more than one prompt, in 2 out of 2 annual meetings.
- The student will prepare a short self-presentation (written, verbal, or multimedia) to share at their IEP meeting, including their goals, accommodations, and future aspirations, with 90% completion as measured by teacher checklist.
- Prior to the IEP meeting, the student will review their current goals and identify one goal they feel they’ve met and one they’d like to change, with support, in 3 out of 4 planning sessions.
- The student will role-play IEP meeting scenarios and practice expressing their preferences or concerns, demonstrating appropriate communication skills in 4 out of 5 practice sessions.
- During IEP planning meetings, the student will ask at least one clarifying question or make one suggestion related to their services or goals, with no more than two prompts, in 2 out of 3 observed opportunities.
Self Advocacy IEP Goals: Self Awareness
- Goal: Demonstrate a knowledge of community resources. Objective: The student will research and compile a list of at least three community resources relevant to their educational or personal needs, providing descriptions and contact information for each resource, as presented to the teacher or support staff for review.
- Goal: Describe personal student strengths accurately. Objective: The student will create a visual or written representation highlighting at least three personal strengths, providing specific examples or anecdotes to support each strength, as shared with the teacher or support staff and displayed in the classroom.
- Given visual prompts and adult support, the student will identify one personal strength and one area of difficulty during a structured classroom activity, in 3 out of 4 weekly sessions.
- During a weekly check-in, the student will name one feeling and explain what triggered it, with 80% accuracy, as measured by a teacher checklist.
- The student will identify and explain two accommodations listed in their IEP and when to use them, in 4 out of 5 opportunities, as measured by teacher observation.
- Given a structured reflection activity, the student will list at least one strength and one challenge related to their learning in 4 out of 5 attempts.
- The student will create a personal learning profile that includes three strengths, three challenges, and two strategies that support their learning, with no more than two prompts, by the end of the semester.
- The student will self-assess their use of accommodations weekly and explain whether they were effective or not, in 80% of opportunities, using a teacher-created rubric.
- The student will describe their disability, how it impacts their learning, and name three accommodations they use, in a written or verbal format with 90% accuracy, as measured by teacher rubric.
- In preparation for a transition meeting, the student will identify three personal strengths and three challenges, and explain how these may impact their future education or employment goals.
Self Advocacy IEP Goals: Requesting and Explaining Accommodations
- Goal: Demonstrate appropriate skills in asking for a curriculum modification and will negotiate the modification with some adult cuing.
- Goal: Demonstrate an understanding of what a learning disability (or other condition if appropriate) is and able to communicate to others how he/she learns best. Objective: The student will research and prepare a presentation explaining their learning disability (or relevant condition), including its impact on their learning and effective strategies for learning, to be delivered to the class or a small group with support from the teacher or support staff.
- Communicate academic strategies or compensation skills that work best for him/her.
- Demonstrate appropriate skills in asking for modification independently.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of their learning strategies and make modifications as needed.
- Assess the effectiveness of learning strategies and make appropriate modifications
- Explain the kind of help needed for a situation. (set the stage for weekly situations)
- Identify a strategy for approaching a learning task (self-monitoring skills will not be in place at this time).
- Communicate/Identify academic strategies or compensation skills that work best for him/her.
- Identify one or two curriculum modifications (I need to have more time to complete work, I need to have directions written on the board)
- Explain and communicate one or two environmental needs (I need to sit in the front of the class, I need a quiet place to work) and/or why they are needed.
- Identify one or two learning strategies that they use.
- Student can identify specific curriculum modifications that are in the IEP and why they are needed (My listening skills are not as strong, so I will need a note taker)
- Share with an adult that the IEP is a legal document and what kinds of information can be found on the IEP.
Self Advocacy IEP Goals: Problem Solving
- Given a challenging situation to solve, student will define the problem and come up with at least two possible solutions to the problem in four out of five trials.
- Demonstrate a knowledge of community resources.
- Share work and accept help from an adult (this is a good one for ODD)
- Self identifies that they need assistance and know who is appropriate to ask for help and ask for help.
- When faced with a classroom-related challenge, the student will identify the problem and generate at least two possible solutions, selecting one to try, in 4 out of 5 opportunities with no more than one prompt.
- During structured problem-solving activities, the student will describe the problem, brainstorm options, and evaluate the outcome using a graphic organizer in 80% of opportunities.
- The student will use a self-advocacy script or checklist to work through peer or academic conflicts, choosing an appropriate strategy to resolve the issue in 3 out of 4 observed situations.
- Given a challenging social or academic situation, the student will ask for help or request a strategy (e.g., sensory break, alternate setting) in 4 out of 5 opportunities, as measured by teacher observation.
- The student will reflect weekly on a problem they encountered, describe how they handled it, and identify what they might do differently next time, with 90% accuracy as measured by completed reflection logs.
Communication and Asking for Help IEP Goals
Do Self Advocacy IEP Goals fall under speech therapy? IDEA does not define who is responsible for self advocacy goals for an IEP. It can be anyone. I have found that it is often the speech therapist or special education teacher who does this. Or, another IEP team member who has a good relationship with the student and the student trusts them.
Working on self advocacy and self awareness requires a level of vulnerability, so it is essential that it’s a trusted adult. Best practice would be to ask the student to self advocate and tell you who they’d like to work with on their self advocacy IEP goals.
- Goal: Student will demonstrate appropriate skills in asking for help at appropriate times.
- Goal: Communicate academic strategies or compensation skills that work best for him/her. Objective: The student will compile a list of two academic strategies or compensation skills that have proven effective for them, providing examples and explanations for each, as demonstrated through written or verbal communication with the teacher or support staff.
- By [date], when faced with a problem or task beyond my abilities, I will raise my hand and request assistance from a teacher or peer in [percentage] of opportunities across all settings.
- By [date], when encountering difficulty with a task, I will independently identify the need for help and request assistance from an appropriate adult or peer in [percentage] of instances across different environments.
- By [date], when unsure of how to complete a task, I will use a predetermined signal (e.g., raising hand, asking verbally) to indicate my need for assistance with [percentage] accuracy in various situations.
- By [date], I will utilize appropriate language and communication skills to express my need for help or clarification during classroom activities in [percentage] of instances across all subjects.
- By [date], I will demonstrate understanding of when to seek help by asking relevant questions or seeking clarification in [percentage] of situations across different academic and social contexts.
- By [date], I will utilize a variety of communication strategies (e.g., verbal, written, nonverbal cues) to request assistance when faced with challenges across all subjects, achieving [percentage] accuracy.
- By [date], I will develop and implement a personalized plan for seeking help, which includes identifying appropriate sources of assistance and utilizing them effectively in [percentage] of opportunities across multiple settings.
- By [date], I will independently recognize situations where assistance is needed and effectively advocate for myself by requesting help from an appropriate adult or peer in [percentage] of relevant instances.
- By [date], I will demonstrate improved self-awareness by proactively seeking help when encountering difficulty, as evidenced by an increase in the frequency of help requests by [percentage].
- By [date], I will participate in role-playing scenarios and social skills training exercises to practice asking for help in various situations, demonstrating improvement in my ability to seek assistance across different contexts.
- By [date], I will develop and implement a self-monitoring system to track instances where I successfully seek help and reflect on strategies used to improve my ability to ask for assistance in [percentage] of cases.
- By [date], I will utilize visual aids (e.g., cue cards, posters) to remind myself to ask for help when needed and demonstrate consistent use of these tools in different environments with [percentage] accuracy.
- By [date], I will engage in cooperative learning activities and group projects, actively seeking assistance from peers and teachers as needed, achieving [percentage] of collaboration goals.
- By [date], I will participate in social skills groups or counseling sessions to develop confidence and assertiveness in asking for help, demonstrating increased comfort and efficacy in seeking assistance.
- By [date], I will identify and practice appropriate strategies for seeking help in emotionally challenging situations, such as managing frustration or anxiety, achieving [percentage] success in applying these strategies.
- By [date], I will demonstrate progress in initiating conversations with adults and peers to request assistance, showing improvement in my ability to communicate needs effectively in [percentage] of interactions.
- By [date], I will develop a repertoire of phrases and scripts to use when asking for help, practicing these language skills across various scenarios and achieving [percentage] accuracy in communication.
- By [date], I will actively participate in goal-setting meetings with teachers and support staff, advocating for my need for assistance when necessary and contributing to the development of strategies to address challenges.
- By [date], I will utilize technology tools and resources (e.g., assistive technology, online tutorials) to seek help and access information independently, demonstrating proficiency in navigating these resources in [percentage] of cases.
- By [date], I will generalize the skill of asking for help beyond the classroom setting, applying strategies for seeking assistance in extracurricular activities, community events, and social gatherings with [percentage] success.
- Student demonstrates skills that they know when or how to ask for help.
Self Advocacy Goals and Objectives for High School Students
- Student will demonstrate knowledge of student strengths, areas of need, personal learning style and their applications in daily school, community life and career options.
- Develop an understanding and verbalize what supports they need to be a good employee (address EF skills, etc).
- Explain your understanding of Rehabilitation Act 504 (for students attending college)
- Given five elective class options, student will select one class per semester for schedule.
- Participate in the development of a post-secondary plan.
Self Advocacy Goals and Objectives: Elementary
Here are eight examples of self-advocacy IEP goals and objectives for elementary students:
- Goal: The student will demonstrate the ability to identify personal strengths and weaknesses.
- Objective 1: By the end of the school year, the student will create a list of three personal strengths and three areas for improvement, with 80% accuracy, as assessed by teacher observation and self-assessment.
- Goal: The student will effectively communicate their needs and preferences in the classroom setting.
- Objective 1: During group activities, the student will raise their hand and express their opinions or preferences at least twice per class session, as observed by the teacher, over the course of the school year.
- Objective 2: The student will use a communication notebook to write at least one question or concern per week to the teacher, demonstrating effective written communication skills, with 70% accuracy, as measured by teacher review.
- Goal: The student will actively participate in the development of their Individualized Education Program (IEP) goals and accommodations.
- Objective 1: During IEP meetings, the student will articulate at least one personal goal related to their academic or social-emotional development, with support from the teacher or advocate, as observed by meeting participants, by the end of the school year.
- Objective 2: The student will review their current IEP accommodations and suggest at least one new accommodation based on their needs and preferences, with guidance from the teacher, by the end of each semester.
- Goal: The student will seek assistance when encountering academic challenges.
- Objective 1: When faced with a difficult assignment, the student will ask the teacher for clarification or assistance at least three times per week, as observed by the teacher, throughout the school year.
- Objective 2: The student will use a visual cue (e.g., raising a colored card) to signal when they need help during independent work time, with fading prompts as appropriate, achieving independence in seeking assistance by the end of the school year.
- Goal: The student will advocate for appropriate accommodations and modifications in the classroom.
- Objective 1: The student will independently request a preferred seating arrangement or assistive technology tool when needed, with verbal or written communication, with 80% accuracy, as assessed by teacher observation, by the end of the school year.
- Objective 2: During assessments, the student will remind the teacher of their approved testing accommodations, such as extended time or use of a calculator, demonstrating awareness and self-advocacy skills, with 90% accuracy, as observed by the teacher, by the end of the school year.
- Goal: The student will demonstrate understanding of their learning style and preferences.
- Objective 1: The student will complete a learning style inventory assessment and discuss the results with the teacher, identifying at least two preferred learning strategies, with 70% accuracy, by the end of the first semester.
- Objective 2: Using a graphic organizer or checklist, the student will self-monitor their engagement and productivity during independent work time, adjusting their approach based on their learning preferences, with guidance from the teacher, achieving independence by the end of the school year.
- Goal: The student will practice problem-solving skills to overcome obstacles.
- Objective 1: When encountering a challenging task or situation, the student will independently generate at least two possible solutions and evaluate the consequences of each, with guidance from the teacher, achieving independence in problem-solving by the end of the school year.
- Objective 2: The student will participate in role-playing scenarios or social stories to practice assertive communication and conflict resolution skills, demonstrating understanding and application in real-life situations, with 80% accuracy, by the end of the school year.
- Goal: The student will develop self-confidence in their abilities.
- Objective 1: The student will engage in self-affirmations or positive self-talk daily, either independently or with teacher support, demonstrating improved self-confidence as observed by the teacher, by the end of each marking period.
- Objective 2: The student will participate in extracurricular activities or projects outside of their comfort zone, gradually expanding their skills and interests, with encouragement and support from the teacher, achieving increased self-confidence by the end of the school year.
These goals and objectives can be tailored to meet the specific needs and abilities of individual students, and progress should be regularly monitored and documented through ongoing assessment and feedback.
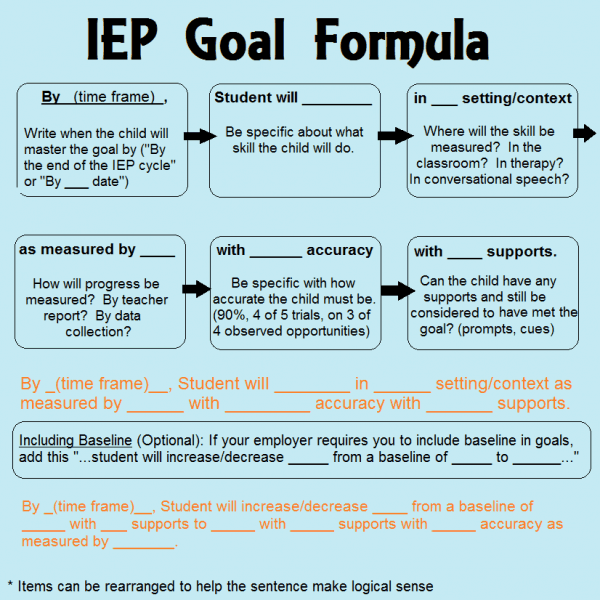
Components of a Strong Self-Advocacy Goal
Like all IEP goals, self-advocacy goals should be SMART:
- Specific
- Measurable
- Attainable
- Realistic
- Time-bound
They should also be tailored to a student’s age, grade level, and current skill set. Consider the following elements:
- How progress will be measured (teacher observation, self-report, work samples)
- The setting in which the skill will be demonstrated (classroom, IEP meeting, with peers)
- What tools or strategies the student will use (visual supports, scripts, checklists)
Use the IEP Goal Formula below to make an IEP goal measurable.
Self Advocacy Examples
Hope this helps and as always, ask in our forums if you have questions.
Self Advocacy Resources
- Self Advocacy IEP Goals
- How to Teach Self Advocacy Skills
- Student Strengths List
- Free IEP Vision Statement Workbook
- Why all Disabled Students Need Social Capital
- 6 Reasons Your Child Should Attend Their IEP Meeting
- How and Why You Should Talk to Your Child about their Disability
- Effective IEP Transition Planning (beyond food, filth and flowers!)


